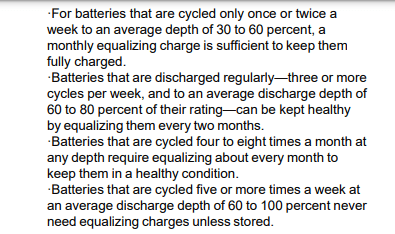
This is your complete guide to forklift battery maintenance.
With decades of combined experience, we know what it takes to keep your batteries in good shape.
In this article, you’ll learn proper forklift battery maintenance and care tips, including:
- How to work safely with forklift batteries
- Charging and regular equalizing procedures
- How and when to check fluid levels, add water, and wash your batteries
Let’s dive in!
There are two types of industrial forklift batteries: Lead-acid and lithium-ion.
Lithium-ion batteries require virtually no maintenance.
Lead-acid batteries, however, must be maintained.
Therefore, most of this article pertains to lead-acid batteries.
Forklift batteries can cause injury or death if not handled safely.
That’s why it’s important to learn proper safety tips when working with them.
Forklift Battery Dangers
Some of the dangers associated with forklift batteries include:
Crushing. Forklift batteries can weigh 2,000 to 5,000 lbs. - or even more. Improper handling can crush fingers, hands, and feet
Chemical burns. Battery acid can spill and cause burns when in contact with the skin
Shocks. Stored electricity in lift truck battery cells can short and electrocute if handled improperly
Explosions. Forklift batteries emit flammable hydrogen gas during charging. An ignition source can cause an explosion if the gasses aren’t vented
Thermal burns. Forklift batteries can operate at high temperatures. Exposure to these temperatures could result in burns
Safety Outside the Battery Area
Battery safety should start with awareness before even entering the battery area.
Here’s what OSHA recommends you do to keep safe:
Keep a phone with you in the charging area. This is for communication in case of an emergency
Wear the right battery operation personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes an apron, goggles or face shield, hard hat, gloves, and safety footwear, among others
Keep distance from the forklift battery while it’s being moved or lifted. This will help prevent physical injuries
Remove all metallic items before entering the charging area. This includes everything from tools to jewelry to avoid the risk of electric shock
Safety Inside the Battery Area
While in the battery charging area, keep in mind the following:
Keep the charging area well ventilated for proper air circulation
Do not lay metallic items on the top of an uncovered battery. This will help prevent sparking and electric shock
Keep open flames away from the battery charging area. That includes not smoking
Keep battery covers open during charging. This helps with proper heat dispersal
Never add water to the battery before charging. Only add water after charging is complete and the battery is cooled
Do not attempt to add acid to a battery. This is a dangerous procedure and should only be performed by professional battery technicians
While attaching or detaching the battery connector, keep the charger unplugged and turned off
If the battery temperature rises or if you see leaks, turn off the charger. Then, restart the charger at a lower charge
If you wash the battery, don’t dump the water down the drain. Dispose of battery water following local and EPA guidelines
Leave major battery repairs to professionals
Follow these tips and you’ll be better protected from the hazards inherent with forklift batteries.
With that out of the way, let’s move on to the five key areas of battery maintenance.
Industrial environments and all the hazards that go with them can cause forklift batteries to take a beating.
To catch anything wrong with your batteries before they become bigger problems, you should regularly inspect them.
Overall, this should include checking the:
Battery case
Connectors
Cables and tips
Intercell connectors
Vent caps
We’ll go through each one below.
Battery Case
Some of the problems that can develop with battery cases include rust, impact damage, and corrosion.

When inspecting a battery case, you should check for these ailments and document them.
If they get worse, you may need to have the battery case replaced.
Additionally, it’s common to see a build-up of a white, powdery substance.
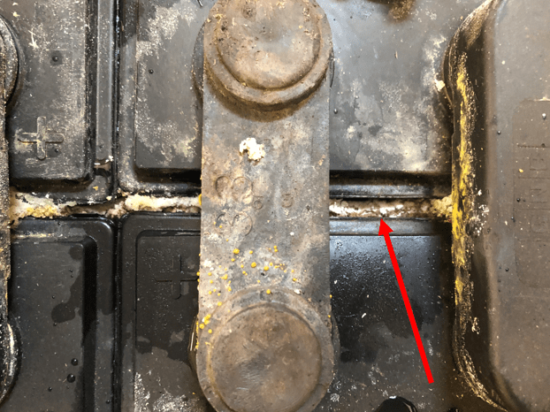

This is sulfation coming from inside the battery cells.
If you see this, go ahead and wash it off with an acid-neutralizing agent.
Connectors
Battery connectors are made of plastic.
As such, they’re liable to be cracked and broken with ease.
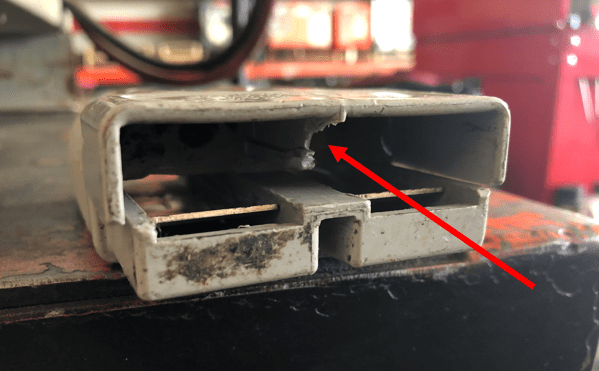
They’re also susceptible to heat deformity.
That’s why you should check the connector housing and replace it if it’s damaged or deformed.
But because replacing connectors carries a high risk of electric shock, it’s best to leave this to a battery professional.
Cables and Tips
Battery cables are covered in a thick rubber shield to protect them from damage and to limit the risk of electrical shock.
But they’re also liable to wear and damage.

Likewise, cable tips can degrade over time.

If the wire cable wire is exposed, or if the tips are worn, they should be replaced.
These tasks can be dangerous, so you should hire a battery professional to get the job done.
Intercell Connectors
Another component that’s liable to corrosion is the intercell connectors.

Over time, these can get eaten away, reducing the conductivity between the battery cells.
If you notice these parts degrading, schedule to get them replaced by a battery technician.
Vent Caps
These plastic knobs cover the water inlets on each cell.
It’s easy for those watering batteries to forget to replace them once they’re finished.

That’s why you should check to see that each cap is in place and secure.
Go ahead and replace them if they’re missing.
A quality forklift battery preventative maintenance program includes proper charging.
This helps improve your forklift battery’s useful lifespan and reduces maintenance requirements.
How much and how long you charge your forklift battery depends on:
Your forklift’s operating hours
The type of forklift battery
The battery capacity
Your preferred charging method
The more hours a forklift is in operation, the higher the battery consumption.
Thus, the more frequently you’ll need to charge the battery.
Depending on your type of forklift battery (lead-acid or lithium-ion), there are three charging methods you can use:
- Conventional charging
- Opportunity charging
- Fast charging
Below is an outline of conventional charging vs. opportunity charging vs. fast charging to help you understand the difference.
Conventional Charging
This method has long been the standard way to charge a lead-acid forklift battery.
In conventional battery charging, the battery is recharged at 16 to 18 amps per 100 amp hours for 8 to 10 hours.

And it stops when the battery has reached a 100% charge level.
At that point, the battery must be allowed to cool for 8 hours before it can be used again.
Otherwise, operating under high temperatures can damage the battery’s plates.
Opportunity Charging
With this method, the battery is charged at a higher rate of around 25 amps per 100 amp-hours.

Charging is done whenever there’s time available, like during lunch breaks and shift changes.
Unlike conventional charging, opportunity charging only brings the charge level to around 80 to 85% capacity.
Then once per day, the battery will need to be brought to a 100% charge.
Fast Charging
This method charges the battery at 40 to 60 amps per 100 amp-hours.
Like opportunity charging, fast charging is done whenever there are breaks in operations to allow it.
Also like opportunity charging, fast charging only brings the state of charge to 80 to 85%.
As such, fast-charged batteries must be brought to a 100% charge and equalized once per week to preserve their integrity.
Which Charging Method Should You Use?
Determining the best charging method depends on a few things:
What type of battery you’re using
How much up-time you require
Your tolerance to battery damage
If you’re using lead-acid batteries, conventional charging is the best way to go.
That’s because this method produces less heat than the other two.
And the less heat the battery experiences, the less thermal damage it will suffer.
As a result, the battery will last longer than the other two methods.

That said, if you’re okay with replacing your lead-acid batteries more frequently, you can certainly use an opportunity or fast charger.
On the other hand, if you’re using a lithium-ion battery, opportunity and fast charging are perfectly fine.
Since lithium-ion batteries don’t experience the same ill effects as lead-acid batteries do during opportunity and fast charging, they won’t deteriorate in the same way.
Overall, if you’re running a single shift operation, it’s better to use conventional charging.
If you have a multi-shift operation, it’s best to use opportunity or fast charging.
When Should You Charge Your Forklift Battery?
The right time to charge your battery is when it’s discharged 20 to 30%.
Waiting any longer will not only damage the battery cells but also increase maintenance costs and shorten the battery’s useful lifespan.
And remember never to interrupt a charge cycle.
Why?
A lead-acid battery has a limited number of charges, usually around 1,500.

But it can’t distinguish between full or half-charging.
So partially charging the battery still uses up a charging unit from its “bank.”
Also, deep-discharging can cause overheating on the truck’s electrical components.
And that can damage your lift truck.
Another advantage of lithium-ion batteries is that they equalize automatically.
So this section applies exclusively to lead-acid batteries.
Essentially, equalizing or equalization charging is a forced overcharge.
This is done by increasing the charging voltage to 110% of the recommended level to cause the battery to gas and bubble.
Regular equalizing is necessary because of two things that happen as you use your battery:
- Lead sulfate crystals attach to the battery plates and harden. This is called sulfation:

2. The electrolyte (acid-water mixture) separates and the acid settles at the bottom of the battery. This is called stratification.
Sulfation and stratification make the battery’s cells lose their capacity to hold a full charge.
The result is that your battery becomes less efficient.
Battery equalization helps to reverse this situation.
But how?
Through bubbling and gassing in the battery’s cells, it:
In a nutshell, equalization is important because it helps maintain battery power capacity and longevity.
Removes lead sulfate crystals from the battery plates before it hardens. In other words, it breaks up sulfation
Remixes the battery’s water-acid mixture. This rebalances the electrolyte concentration and reverses stratification
How Often Should You Equalize Your Battery?
In general, you should equalize your battery once per week.
But, the frequency can depend on both your battery manufacturer and how often you use the battery.
So it’s best to consult your owner’s manual to find out what they recommend.
Additionally, it can be to your advantage if you perform equalization charges when operations are slower.
For example, many businesses equalize their batteries on the weekend.
That way, they can fit in the extra charging and cooling time without disrupting operations.
How Do You Equalize Your Battery?
The proper way to equalize your battery is to use a battery charger that has an equalizing setting.
While many forklift battery chargers can do this automatically, not all chargers offer this functionality.
It’s simple to tell if your charger can equalize.
Just look for a button that says “Equalize.”
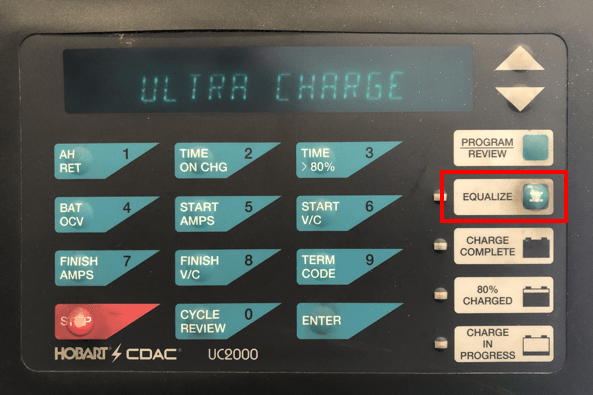
Then, it’s just a matter of plugging the battery in, hitting the button, and waiting until the charge completes.
If you’re looking for a maintenance-free forklift battery, lithium-ion is the way to go.
That’s because they’re sealed, and don’t require watering or equalizing.
But lead-acid battery forklift maintenance must include checking and maintaining your fluid levels regularly.
This is because lead-acid batteries generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction.
To achieve this reaction, the battery is filled with lead plates and electrolytes (a mixture of sulphuric acid and water).
The lead plates and sulphuric acid are chemical reactors, while water protects the battery’s active material while it generates power.
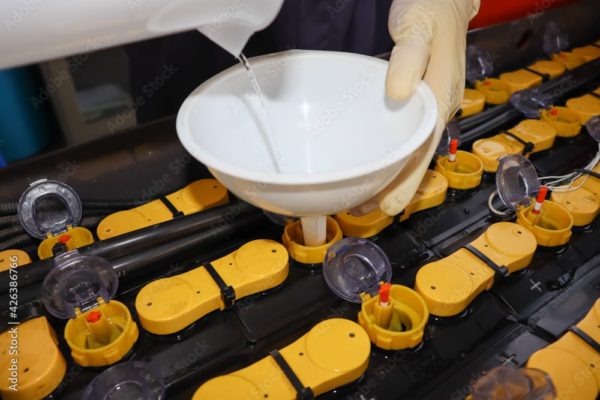

But if the water level dips too low, the plates will be uncovered.
And this loss of protection will degrade the plates and shorten the battery’s lifespan.
In addition to checking the water levels, you should also check the specific gravity of each cell.
It should be around 1.285.
Not sure what specific gravity is?
It’s the ratio of water to battery acid.
If the specific gravity is low, that means there’s more water than acid.
If it’s high, there’s more acid than water.
In either of these cases, the battery won’t perform as well as it should.
To check the specific gravity, you need to use a hydrometer.
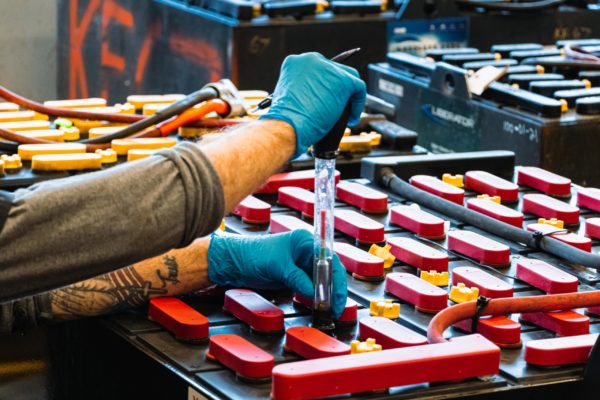

Simply open the cell cap and draw enough fluid into the hydrometer so that the float rises.
Do this for each cell, then record the readings in your battery maintenance log.
And remember: If acid levels need to be adjusted, contact a professional for assistance.
When Should You Add Water to Your Forklift Batteries?
The correct time to add water to a battery is after charging or equalizing the battery.
This is when the battery’s water level is at its highest, and it will prevent a boilover.
You will also get the opportunity to see the level so you can top it off.
Before you water your battery, check two to three cells to confirm that there is enough fluid to cover the lead plates.
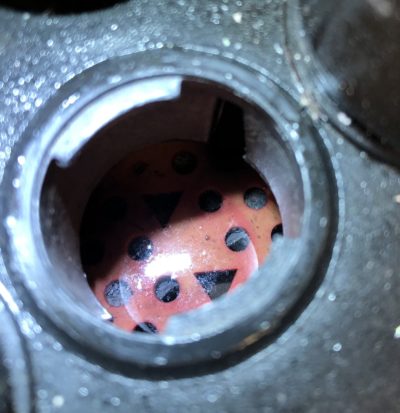

If you’re unsure, you can check all of the cells.
If there’s not enough fluid, add water to the battery.
But you shouldn’t use regular tap water.
Instead, use distilled or deionized water with a pH level between 5 and 7.
How Often Should You Water Your Batteries?
Adding water to your forklift battery should be done every five to ten charging cycles.
But you should check your manufacturer’s recommendations to confirm how often.
If you water your forklift battery too frequently, it may experience electrolyte boilover.
And this may reduce its capacity by 3%.
On the other hand, if watered infrequently, it can cause permanent damage to the battery and possibly the lift truck.
How Much Water Should You Add to the Battery?
It's recommended that you add just enough water to cover the plates.
You never want to overfill your forklift battery with water because it can overflow.
When this happens, electrolytes and sulfuric acid can spill out, exposing you to chemical burns.

So, when adding water to your forklift battery, leave enough space for the fluids (water and sulfuric acid).
That way, the fluids can expand when the battery is charging or in use.
Yet another advantage of lithium-ion forklift batteries is that they will not leak dangerous fluids.
As such, you don’t need to worry about cleaning the case to get rid of corrosive acid.
But lead-acid batteries must be kept clean through regular washing.

Not doing so can allow battery acid residue to build up on the battery.
And that can cause all kinds of problems, like:
Acid burns
Damage to equipment through corrosion
Damage to clothing
By washing your forklift batteries regularly, you’ll gain many benefits, including:
Reducing workplace hazards from battery fluids (sulphuric acid) leaked or overfilled on the battery edges
Extending the battery’s useful life
Improve battery’s charge time by reducing electrolyte build-up on charging terminals
To wash your battery case, use an acid-neutralizing de-greaser or warm water.
You can either spot clean the battery’s top or wash the entire battery assembly.
Just remember to ensure that all the battery’s vent caps are tightly sealed before you begin.
This will prevent the cleaning solution from seeping into the electrolyte, which can ruin your battery.
How Often Should You Wash Your Forklift Batteries?
It depends on how often you use the battery and how dirty your operation is.
But in general, you should check the battery weekly for signs of corrosion.
Then spot-clean them if found.
You should also clean the battery edges and case every month.
Plan to clean the entire battery case as part of your annual battery maintenance duties.
If it’s warranted, you can do this more frequently at 3 to 6 months.
As you now know, proper electric forklift battery maintenance and care can help extend its useful life and improve its longevity.
So, here’s a forklift battery maintenance procedures checklist to make doing so a little bit easier.
Keep in mind that because lithium-ion batteries are virtually maintenance-free, these checklist items mostly apply to lead-acid batteries.
What Is the Typical Forklift Cost for Annual Battery Maintenance?
Many factors go into calculating battery maintenance costs, including:
- Watering frequency
- Washing frequency
- Number of batteries
- Basic repair costs (cable replacements, etc.)
But a good price range is $800 to $2,000 per year.
You can get a more accurate cost estimate by using this handy (and free) forklift battery maintenance calculator.
Alternatively, contact Foxtron for an estimate tailored to your needs.
Inspecting
Check the battery case, connectors, cables and tips, intercell connectors, and vent caps. They should be present and undamaged. Have a professional repair or replace them if needed
Charging
Only charge batteries in designated areas
Keep open flames and metals away from the battery top during charging
Avoid opportunity charging. Doing so uses one of the battery’s cycles each time you connect it to a charger
Charge the battery only when it is at most 80% discharged
Only use appropriate chargers with the correct voltage and current output
Don’t prematurely end charging. Allow the battery to reach 100% capacity before disconnecting
Wait for the battery to cool down before using it again
Make sure to keep the truck compartment and battery cover open during charging. This will allow gasses to safely vent
Equalizing
Use a charger that has an equalizing setting
Put the battery on an equalizing charge weekly
Clean the battery after equalizing to remove electrolyte spillover
Do not equalize the battery more than the recommended frequency. More isn’t better!
Watering
Water your battery regularly. If possible, set up a weekly or bi-weekly watering schedule to maintain proper water levels
Maintain the correct water level in the battery. That’s about one-half inch below the battery cap opening
Add distilled or deionized water only after the charge cycle
Check the specific gravity. It should be around 1.280 for a fully charged battery. If the gravity is different across cells, try equalizing it. If it’s still low, acid may need to be added
Contact a battery professional when acid needs to be added
Washing
Clean the battery top at least every month. Clean the entire battery at least every 3 months
Use warm water and acid-neutralizing de-greaser when cleaning
Dispose of wastewater according to local and EPA regulations
Conclusion
There you have it. The complete forklift battery maintenance guide.
Now, we’d like to hear from you.
Are you a forklift operator?
If so, what did you learn about forklift battery maintenance that we’ve discussed here?
Let us know in the comments section below!