This article explains everything you need to know about gel batteries vs. lead-acid batteries.
There’s much confusion about these two types of batteries.
So we hope this will clear it up.
In this article, you'll learn:
- The relationships between gel, AGM, and lead-acid batteries
- The advantages and disadvantages of each battery
- How to charge gel batteries
- The answers to common questions about each battery
Let's dive in!
Lead-acid batteries are the most common in the market.
But, there are several variations of lead-acid batteries, including:
- Flooded
- Sealed. These are also called valve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA) or sealed lead-acid (SLA) batteries
Usually, when talking about lead-acid batteries, people mean flooded lead-acid.
Whereas, gel and AGM batteries are types of sealed batteries.
So Is a Gel Battery Lead-Acid? And Are AGM Batteries Lead-Acid?
The answer to both questions is yes.
To recap, AGM, gel, and flooded batteries are all types of lead-acid batteries.
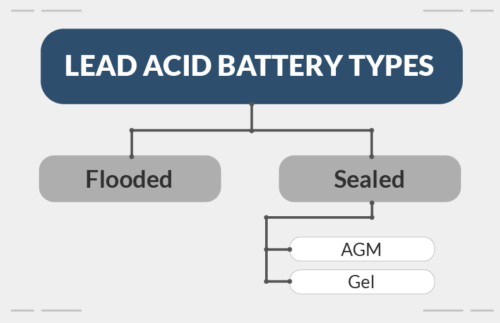
For the most part, the contents and electrochemical workings of these lead-acid batteries are very similar.
But there are some important differences, which we’ll cover next.
What’s the Difference Between Flooded and Sealed Batteries?
The main difference between flooded batteries and sealed batteries is the electrolyte.
Flooded batteries are filled with a liquid electrolyte solution.

On the other hand, sealed batteries have a solid electrolyte.
AGM batteries are filled with a glass mat substance.

And gel batteries are filled with silica to coagulate the electrolyte.

Besides that, sealed batteries are virtually immune from spills and leakage.
As a result, they can be used in any position or orientation without worry.
But flooded batteries are not sealed and thus liable to spills and leakage.
Furthermore, they require regular watering.
Conversely, sealed batteries do not.
And that makes them virtually maintenance-free.
Invented in 1860, rechargeable flooded lead-acid batteries are the most common and widely used type of lead-acid battery.
Flooded batteries are composed of alternating lead and lead oxide plates along with liquid electrolytes (sulfuric acid and water).
Using an electrochemical process, these components react to produce energy.
How Do Flooded Batteries Work?
First, they are called "flooded batteries" because the liquid electrolyte is free to move within the cell.
What does that mean?
Inside the cell, the alternating lead plates are immersed in the electrolyte solution.
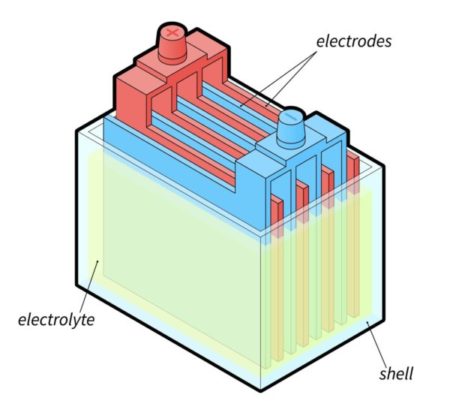
As the electrical current passes through the battery, the electrolyte interacts with the lead plates.
The plates are then converted into lead sulfate.
And it’s through this reaction that chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
But this process is reversed once the battery is charged.
The charging breaks down the lead sulfate, turning it into pure sulfuric acid and lead.
Also, the water in the electrolyte splits, and hydrogen gas is released.
So, to prevent the hydrogen gas build-up (and avoid battery explosions), flooded batteries have a vent to exhaust the gas and relieve the pressure.

But this process also leads to water loss.
That’s because the hydrogen doesn’t have a chance to recombine with oxygen and settle back into the electrolyte solution as water.
Thus, it creates a need to regularly water the battery.
This process is why, although they are the cheapest, flooded batteries require more battery maintenance.
The user must access individual cells and top them up using distilled water as the battery dries out.
Flooded Battery Advantages
Widely available
Relatively cheap
Available in different sizes and capacity
Provides good deep-cycle performance
Flooded Battery Disadvantages
Requires regular watering and strict maintenance
Requires charging in designated and ventilated rooms
Liable to cause injury and corrosion due to spills and leakage
Requires the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling
Vents out substantial quantities of flammable hydrogen gas
Easily damaged if left to over-charge
Prone to high self-discharge rate
Considered hazardous material when transporting
What Are Flooded Batteries Used For?
Large flooded batteries are often used in industrial equipment, like forklifts.
Additionally, they’re a popular solution for cars, solar power energy, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
How Do Gel Batteries Work?
As the name suggests, gel cell batteries are fitted with an immobile and highly viscous electrolyte.
This jelly-like electrolyte is composed of silica and sulfuric acid.
The gel is similar to silicone gel in appearance and composition and is used as a thickening agent.

This helps to enhance the gel-type battery’s internal structural integrity.
And it holds the lead plates and active material in position.
How?
The gel 'glues' onto the lead plates, essentially combining the electrolyte and plates into one single piece.
Sealed gel batteries are also recombinant batteries.
This means that the negative plate absorbs the oxygen produced on the positive plate during discharge, thanks to the seal and the pressure valve.
Now, instead of producing and releasing hydrogen gas, the negative plate produces water.

This prevents water loss and maintains the battery's water content.
For these reasons, gel battery maintenance is virtually non-existent.
Gel Battery Advantages
Maintenance-free, with no need for regular watering
Spill- and leak-proof
Can be mounted in any position
Offer more resistance to extreme temperatures
Better withstands shock and vibration
Classified as non-hazardous materials for road transportation
Offers extremely low self-discharge rates
No gassing, making them safe to install in places with limited ventilation
They do not experience corrosion
Offers excellent deep-cycle performance
Can be installed or used near sensitive electronic equipment
Gel Battery Disadvantages
More expensive than flooded lead-acid
Sensitive to overcharging. Requires special SMART chargers and regulators
What Are Gel Batteries Used For?
Gel batteries are used in low power demanding equipment like:
- Floor scrubbers and sweepers
- Walkie pallet jacks
- Wheelchairs
- RVs
- Cars
- Boats
- Cell phones
How Long Can a Gel Battery Last?
The answer to this question depends on:
- How it's charged
- How it’s used
- The working temperature
- The charge capacity
If you charge a normal 12-volt gel battery to 90% charge capacity and keep it unused in the charged state, it will last up to 6 years and while retaining up to 80 % of its original capacity.
Now, what is the life expectancy of a gel battery?
Gel batteries can last up to 20 years with up to 5,500 charge cycles.

Compared to flooded batteries’ 1,000 to 1,500 charge cycle (3 to 5 year) lifespan, that’s much longer.
And that’s because gel batteries resist sulfation and are maintenance-free.
Charging Gel Batteries: Everything You Need to Know
Charging gel batteries is a little more complex than charging flooded lead-acid batteries.
Here's what you need to know...
You’ll first need a specialized gel battery charger (or SMART charger).
Why?
Because gel batteries are susceptible to voltage spikes.

And these specialized chargers have specific settings that prevent these spikes.
Secondly, when charging a gel battery, you need to give it extra time.
That’s because gel batteries require slow, constant voltage charging cycles.
And charging the battery at the wrong voltage can damage it, cause battery failure, or shorten its lifespan.
Third, you'll need to constantly monitor the charging process and take off the charger as soon as charging is complete.
If you don’t, you can create pockets in the electrolyte.
And this can cause irreversible damage to the battery.
Can You Charge a Gel Battery With a Regular Charger?
Yes, you can.
But, charging gel batteries with a flooded lead-acid charger is risky.
Why?
Gel batteries like to be charged slow and low.

So, when charging a gel battery with a lead-acid charger, you must be extra cautious.
Ensure that the peak charging voltage does not exceed 14.7 volts.
Otherwise, you can end up with a dried-out, non-conductive gel.
How to Charge a Gel Battery With a Regular Lead-Acid Charger
-
Attach the lead-acid battery charger to your gel cell battery. Ensure you connect the terminals correctly. The red cable goes to the positive terminal. And the black cable goes to the negative terminal
-
Switch the charger settings to deep cycle (for example, to 2 amp /12 volt). This will help mimic the charging characteristics of a constant voltage charger (CVC) that is used to charge deep cycle gel batteries
-
Next, switch the charger to manual instead of auto. If you leave it on auto, it may taper its voltage when the battery reaches full charge
-
Now, monitor the battery closely as it charges for 7 to 12 hours. Make sure the voltage output never exceeds 14.7 volts
-
Once the battery charging reaches 95%, remove the charger
How Do AGM Batteries Work?
First, the composition of AGM batteries looks likes this:
- Fiberglass mats
- Lead plates
- Electrolyte
- Pressure control valve
The microfibre fiberglass mats, placed between the lead plates, absorb and immobilize the electrolyte.
The glass mats also act as separators and insulators between the positive and negative plates.
This design is what makes AGM batteries spill-proof.

Like gel batteries, AGM batteries are recombinant.
What does this mean?
The safety pressure relief valve prevents the release of hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Instead, they’re able to recombine during charging.
And this helps prevent subsequent water evaporation from the cells.
Also, the glass mats wrapped around the battery's positive plate help prevent damage from vibration and impacts.
They also help extend its cycling.
Plus, AGM batteries have a lower internal resistance.
This lower resistance reduces losses to heat as power flows through the system.
And that’s why AGM batteries have more output voltage and lower charging times.
AGM Battery Advantages
Sealed, allowing gasses to recombine and eliminating the need to add water
Maintenance-free
Spill- and leak-proof design. There’s no mess while charging and no corrosion risks
Impact-resistant and greater vibration resistance, reducing battery failures
Superior cold-weather performance
Well suited for high current applications
Little internal resistance for more power output. That means less charging time and reduced losses due to heat
Not considered hazardous material
Do not require ventilation
Flexibility to mount in any position or orientation
AGM Battery Disadvantages
Higher initial cost than flooded batteries
Performance suffers in warmer temperatures. Most AGM manufacturers recommend stopping the charge after 120°F (49°C)
Sensitive to overcharging
What Are AGM Batteries Used For?
AGM batteries can be used in many of the same applications as gel batteries.
Some popular uses include:
- Cars
- Boats
- Snowmobiles
- Motorcycles
- ATVs
- Solar power
Are All AGM Batteries Deep Cycle?
No, not all AGM batteries are deep cycle.
But many are.
After all, they do have a greater ability to deep cycle discharge.
In fact, AGM batteries' specified depth of discharge (DoD) stands at 80% compared to the 50% DoD of flooded batteries.
Moreover, they can charge up to 5 times faster than flooded batteries.
Do AGM Batteries Last Longer?
An AGM battery can generally last between 3 and 5 years and up to 8 years if the battery is used properly.
That’s about two to three times longer than a flooded battery.
But overall, their lifespan depends on several factors, including:
- How it's charged
- How it’s used
- The working temperature
If these items are done improperly, that will shorten the battery’s useful life.
Are AGM Batteries Better Than Gel Batteries or Flooded Batteries?
The fact is, AGM batteries are better than flooded batteries - if you’re prepared for the extra cost.

However, they are comparable with gel batteries.
Despite their different composition, both offer benefits like:
Better charge capacity
Prevention of spillage and leaks
Better electrolyte volume
Superior life expectancy
No maintenance requirements
Overall, the debate between AGM vs. gel batteries comes down to your budget, needs, and what serves you best.
Conclusion
That's it.
You now know the difference between gel, AGM, and flooded lead-acid batteries.
Now, we'd like to hear from you.
Do you use any of these battery types?
Which do you prefer?
Let us know in the comments section!